The University of Michigan’s four-course advanced program, the More Applied Data Science with Python specialization, is available on Coursera and is intended for students who have already finished the foundational “Applied Data Science with Python” series or who have intermediate knowledge of Python and data analysis.
What Will You Learn in This Course?
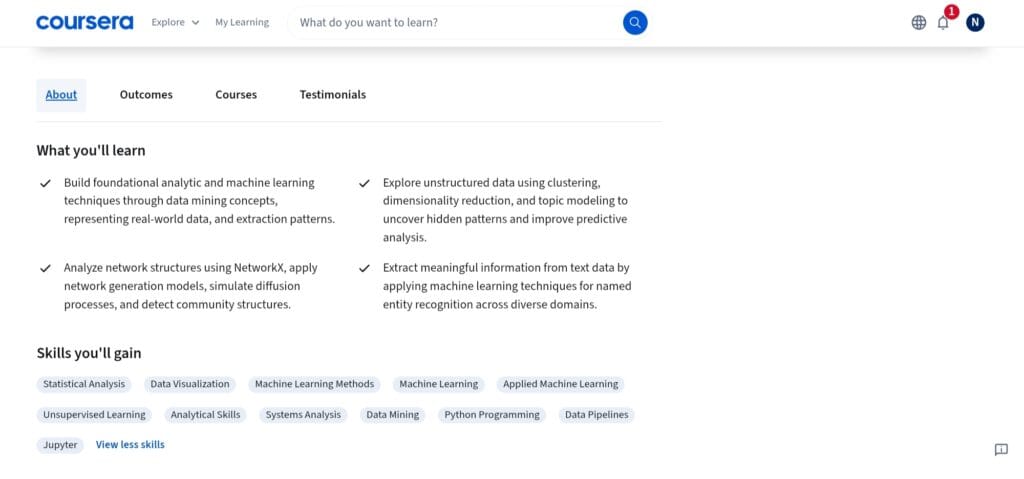
Beyond fundamental machine learning and data wrangling, the specialization delves deeply into sophisticated data science approaches, encompassing fields like network analysis, data mining, and unsupervised learning. What you will learn from each module is as follows.
Advanced Data Mining Techniques
First, you will learn how to use a range of structures, such as itemsets, vectors, sequences, matrices, time series, and networks, to extract meaningful patterns from complex datasets. This course has a strong emphasis on using these strategies in real-world situations, for example –
- Examining transactional data for common trends
- Constructing recommender systems
- Applying sequence analysis to activities that are time-based
- Applying matrix factorization methods to collaborative filtering and dimensionality reduction
The objective is to provide you with the skills you need to extract actionable insights and hidden trends from both structured and unstructured data.
Unsupervised Machine Learning & Topic Modeling
This area of expertise focuses on identifying structure in data without labels, in contrast to supervised learning, which trains models using labeled data. You will learn the following concepts.
- Clustering methods, such as DBSCAN and k-means
- Techniques for reducing dimensionality (like PCA, t-SNE, and UMAP)
- Capturing nonlinear interactions with manifold learning
- Estimating density and identifying anomalies
- Using techniques such as word embeddings (e.g., Word2Vec) and Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) for topic modeling
Finding hidden themes in massive text corpora, segmenting customers, and natural language processing all depend on these methods.
Network Modeling and Analysis
You’ll explore the intriguing realm of networks in this section; consider information flows, biological pathways, and social networks.
The NetworkX package in Python will be used to create and display graphs (nodes and edges), examine node importance, shortest pathways, and centrality metrics, model diffusion processes, such as the dissemination of information or illness, and find modular patterns and community structures in networks.
These abilities are very applicable to domains such as recommendation systems, cybersecurity, social science, and epidemiology.
Hands-On Projects with Real-World Datasets
Practical tasks that test your ability to apply your knowledge to datasets that reflect actual industry issues are a part of every course. Sequence mining using genetic databases is one example.
More examples include social media comments and restaurant reviews for theme modeling, simulations of epidemics with network diffusion, and data about recipes and ingredients for recommender systems and association rule mining.
This practical method guarantees that you are developing a data science portfolio with observable, project-based results rather than merely learning theoretical principles.
What Concepts Are Taught in This Course?
Each of the four closely related courses in the More Applied Data Science with Python specialization focuses on developing advanced Python data science skills. Through these classes, you will gradually get a deeper grasp of important data science techniques that go beyond conventional supervised learning.
1. Data Mining in Python
The groundwork for comprehending pattern recognition and data mining techniques is laid out in this course. You’ll discover the following aspects in this course.
- Find recurring trends and correlations in huge datasets (market basket analysis, for example).
- Make use of algorithms such as FP-Growth and Apriori.
- Utilize sequence mining for data that is time-ordered.
- Examine the usage of collaborative filtering and matrix factorization in recommender systems.
- Recognize interestingness metrics such as support, lift, and confidence.
In order to assist you in linking raw data to downstream machine learning models, it also discusses the useful application of these ideas in recommendation engines and data pretreatment pipelines.
2. Applied Unsupervised Learning in Python
The foundation of contemporary exploratory data research is unsupervised learning. This course will cover the following topics.
- Clustering algorithms include spectral clustering, DBSCAN, hierarchical clustering, and k-means.
- Reduction of dimensions using PCA, t-SNE, and UMAP
- Understanding nonlinear features in high-dimensional data with manifold learning
- Employing LDA, NMF, and Word2Vec for NLP tasks: topic modeling and embeddings
- Techniques for evaluating models without labeled data (such as coherence and silhouette score)
Without requiring labeled results, this course walks you through real-world use cases, including document classification and consumer segmentation.
3. Network Modeling and Analysis in Python
Networks are strong data structures that can be used to represent intricate interactions. You will learn how to use NetworkX to build and modify networks in this course.
Also, you will figure out how to determine the centrality metrics (degree, betweenness, and closeness), model diffusion processes, such as the dissemination of information or infections, find modular structures and communities in big graphs, and examine how random walks and graph traversals behave.
Use examples include developing network-based recommendation systems, researching the transmission of disease, and modeling social networks. This course integrates computational and analytical understandings of the behavior of linked data.
4. Capstone / Applied Project
Using a sophisticated, real-world dataset, you will apply your acquired knowledge in a project-based manner in the last module. You will select a challenging issue requiring network analysis or unsupervised learning.
Then you will create a comprehensive data pipeline that includes results cleansing, modeling, visualization, and interpretation, and present your findings and defend your approach as though you were speaking to a hiring manager or stakeholder.
This final project is a great way to demonstrate your abilities to prospective employers and provide your data science portfolio with a high-level case study.
Who Should Join This Course?
Intermediate Python programmers who are at ease using Jupyter notebooks, NumPy, scikit-learn, and Pandas.
Those who have previously finished the Python specialization in Applied Data Science or have comparable experience. Before beginning this series, it is advised to finish that one.
Professionals or learners who wish to expand their knowledge of network analysis, text and topic modeling, and unsupervised learning.
Will You Get a Job After Completing This Specialization?
The specialization gives you sophisticated modeling and analytical abilities that are in high demand, particularly when it comes to unsupervised machine learning and network data.
It improves employability in positions like data scientist, ML engineer, analyst, or research associate when combined with a portfolio of practical projects created from actual datasets.
It does not, however, ensure employment; rather, success is contingent upon your overall portfolio, interview skills, and relevant work history.
Nevertheless, project-based results and University of Michigan qualifications might be useful in employment pipelines.
How Long Does This Course Take to Complete?
If taken consecutively at a moderate pace, usually 10 to 12 hours per week, the projected total length is 14 weeks. According to Coursera, completing this specialty at a pace of ten hours per week will take four months.
However, because this course is self-paced, you can finish it at your own pace.
How Much Does This Course Cost?
Based on the subscription model of Coursera, the cost can vary. A three-month subscription to this course will cost you around $32 per month (total $96 approx).
Another way to purchase this course is via a Coursera Plus subscription. The subscription costs $59 per month and offers access to 10,000+ courses on Coursera. Also, it comes with a 7-day free trial, allowing you to assess its value before going with the subscription.
Is It Worth Taking the More Applied Data Science with Python Specialization?
This program is an excellent next step if you have completed the core Applied Data Science with Python Specialization or already have intermediate Python abilities.
It expands your toolkit in areas including network topologies, topic analysis, and unsupervised modeling—skills that are becoming more and more important in data science positions. It is preferable to begin with foundational courses if you are a beginner.
FAQ
Is prior experience necessary?
Yes, it is anticipated to have some knowledge of scikit-learn, Python, Pandas, and fundamental machine learning. It is highly advised to finish Applied Data Science with a Python Specialization.
What tools and libraries will I use?
You’ll work primarily in Python, using libraries like:
pandas and numpy for data manipulation
scikit-learn for machine learning
NetworkX for network analysis
gensim, nltk, and spaCy for natural language processing
matplotlib and seaborn for visualizationAll exercises are done in Jupyter Notebooks, which are hosted on the Coursera platform.
Is Coursera Plus worth it for this course?
Coursera Plus may be more affordable if you want to enroll in additional courses (such as the “Applied Data Science with Python” series or Google/IBM certifications). If not, you may just sign up for this specialization on a monthly basis.
Do I need to install anything on my computer?
Probably not. The majority of coding is done in Coursera’s browser-based Jupyter notebooks. You can, however, use Anaconda or Google Colab to duplicate the configuration if you wish to practice offline.
Is there support if I get stuck?
There are forums for every subject, and teachers do occasionally reply. Because the community is vibrant, you’ll frequently discover that peers have already addressed your queries.
Share Now
Related Articles
8 Soft Skills Every Data Scientist Needs to Succeed
What is the Learn SQL Basics for Data Science Specialization on Coursera?
The Data Science Toolkit: 12 Most Used Data Science Tools Every Data Scientist Needs to Know
Discover more from coursekart.online
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.